
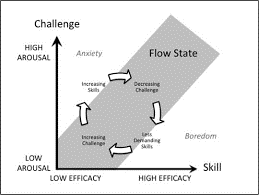
Over a period of time, the researcher can observe certain patterns in behavior.
Flow state psychology series#
Then, participants are asked to answer a series of questions about what they are doing and how they are feeling (Larson and Csikszentmihalyi, 1983). Developed by Csikszentmihalyi and colleague Robert Larson, ESM requires research subjects to be provided with a beeper that beeps at random times during the day. Csikszentmihalyi’s Research & Other Findings on Flowĭiscovery of these six factors of flow is largely due to development of the experience sampling method (ESM). Furthermore, it has been found that people who experience a lot of flow regularly also develop other positive traits, such as increased concentration, self-esteem, and performance. Experience of the activity as intrinsically rewarding, also referred to as an autotelic experience.Ī growing body of scientific evidence indicates that flow is highly correlated with happiness, both SWB (Subjective well-being) and PWB (Psychological well-being).A sense of personal control or agency over the situation or activity.A loss of reflective self-consciousness.Intense and focused concentration on the present moment.He set his life’s work to scientifically identify the different elements involved in achieving such a state. He noted that the act of creating seemed at times more important than the finished work itself and he was fascinated by what he called the “flow” state, in which the person is completely immersed in an activity with intense focus and creative engagement. Csikszentmihalyi began his research on flow by studying artists and creative types (Csikszentmihalyi, 1975). Interestingly, a flow state is characterized by the absence of emotion – a complete loss of self-consciousness –however, in retrospect, the flow activity may be described as enjoyable and even exhilarating!Īccording to one of the scientific pioneers of flow, Hungarian psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, also one of the founders of positive psychology there are six distinguishable factors of flow. You must feel as though you have control and receive immediate feedback with room for growth. Hobbies, such as the image above of competing in chess, are a great example of implementing and experiencing the state of flow. In order for a flow state to occur, you must see the activity as voluntary, enjoyable (intrinsically motivating), and it must require skill and be challenging (but not too challenging) with clear goals towards success. This loss of self-consciousness that happens when you are completely absorbed in an activity – intellectual, professional, or physical – is described in contemporary psychology as a state of flow. Viktor Frankl, who survived a Nazi concentration camp, once said “ What man actually needs is not a tensionless state but rather the striving and struggling for some goal worthy of him” (Frankl, 1992). One may find still greater happiness working towards long-term, meaningful goals. When does this loss of time and total engagement typically occur for you? This could apply to a martial artist completely absorbed in perfecting a flying kick, or a violinist fiercely concentrating on a complex symphony.
Flow state psychology professional#
The Bottom Line: If we are actively involved in trying to reach a goal, or an activity that is challenging but well suited to our skills, we experience a joyful state called “flow.” The experience of flow in both professional and leisure activities leads to increased positive affect, performance, and commitment to long-term, meaningful goals.ĭo you ever find yourself so completely immersed in what you’re doing that you lose track of time? All of a sudden you look up at the clock and realize that hours have passed and you missed dinner time? Think a minute about this. Make a Difference: Change the World, Change Yourself.Symptoms of Anxiety & Anxiety Prevention with Science of Happiness.Top 10+ Coping Skills for Depression You Must Know.
Flow state psychology how to#



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
